Cloud Security
Introduction
Cloud security is a responsibility that is shared between the cloud provider and the customer, independently of whether you are using AWS, Google or Azure.
The Shared Responsibility Model includes three main categories;
There are basically three categories of responsibilities in the Shared Responsibility Model: responsibilities that are always the provider’s, responsibilities that are always the customer’s, and responsibilities that vary depending on the service model: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), or Software as a Service (SaaS), such as cloud email solutions such as Office 365.
The security responsibilities that are always the provider’s are related to the safeguarding of the infrastructure itself, as well as access to, patching, and configuration of the physical hosts and the physical network on which the compute instances run and the storage and other resources reside.
The security responsibilities that are always the customer’s include managing users and their access privileges (identity and access management), the safeguarding of cloud accounts from unauthorized access, the encryption and protection of cloud-based data assets, and managing its security posture (compliance).
Cloud Migrations
- Rehosting also known as ‘lift and shift’ moves your existing physical or virtual servers to cloud without making any major architectural changes.
- Replatforming is about moving applications to the cloud with few optimizations like moving self-hosted infrastructure to managed services.
- Repurchasing is a faster way to access Cloud that involves change of the existing licensing model.
- Refactoring for modifying applications to take advantage of SaaS and PaaS based technology which will aid in cost reduction.
- Retaining few or more on-premise solutions just in case the migration cost is higher than the application’s value is advantageous when depreciation value is achieved before migration.
- Retiring can be done when unused applications are decommissioned or clubbed with other dependent applications to save huge cost
Identity and Access Management for the Cloud
Authentication and access control are two of the capabilities of identity and access management solutions. Cloud IAM allows you to authenticate users no matter where they are and secure access to resources across cloud, SaaS, on-prem and APIs, all the while increasing your speed, agility and efficiency. IAM solutions are available for customers, employees and partners, and can be integrated to provide a complete solution for your enterprise.
With identity verification and access control located in the cloud, the limitations and costs associated with on-premises IAM are replaced by a more flexible, scalable solution. Cloud IAM is key to ensuring security outside of network perimeters and capabilities include:
- Authentication
- Access management
- Directory
- Identity verification
- Consent collection and data privacy management
- Risk management
- Personal identity
- API security
- Self-service for users and developers
Safeguarding cloud accounts
Encryption and protection of cloud-based data assets
Continuous Security
Continuous security involves automating the governance across multi-cloud assets and services, and visualizing this, detect misconfigurations and model and actively enforce best practice security policies.
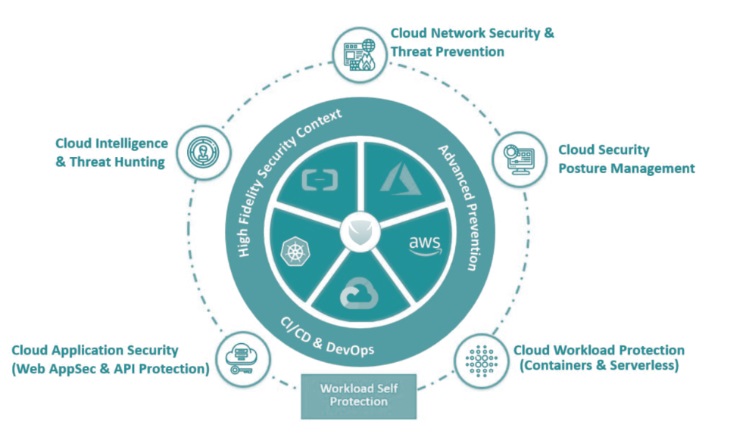
Cloud Intelligence and Threat Hunting
Cloud Intelligence and Threat Hunting provides cloud-native threat security forensics through rich, machine learning visualization, giving real-time context of threats and anomalies across your multi-cloud environment. Detect anomalies, activate alerts, quarantine threats, and remediate threats automatically, utilizing the largest threat intelligence feed.
Know your security posture
Rapidly identify gaps and establish a risk-aligned architecture and roadmap for baseline cloud security that optimizes current technology investments.
Automate native security
Get faster time to value and automate deployment of security guardrails for cloud native services including AWS, Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud.
Be proactive with compliance
Optimize detection and streamline cloud security operations. Mitigate risk with cloud service providers (CSPs) to align with regulatory requirements.
Employ security monitoring and response
Monitor public cloud cost effectively and at scale using security tools and use cases to address evolving threats and complex regulatory requirements.